Asset Performance Management
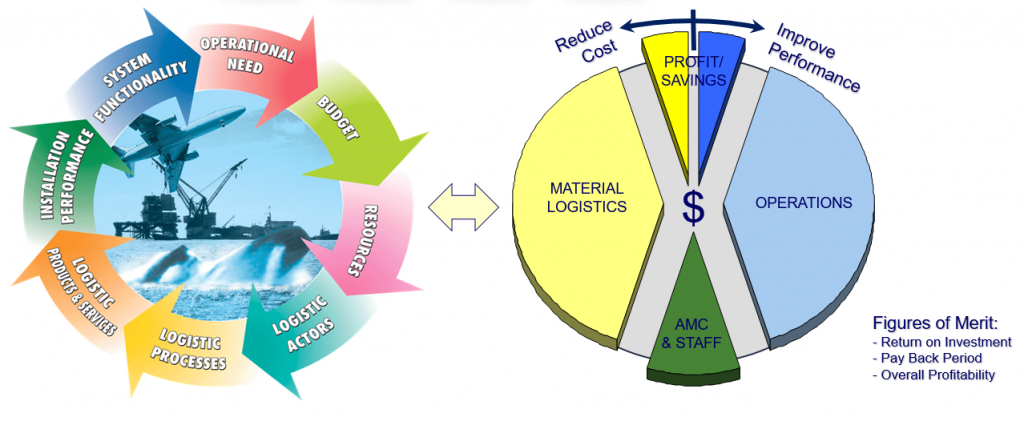
Asset Performance Management (APM) is about setting up the chain in such a way that performance becomes measurable and that these asset (system) performance can be translated into performance of the individual parts / installations of the system. In the reverse order the same principle applies, so that the performance of the individual components / installations can be abstracted to the performance of the system / network as a whole.
Tools
To implement Asset Performance Management in a professional manner, the tools below should not be missed.
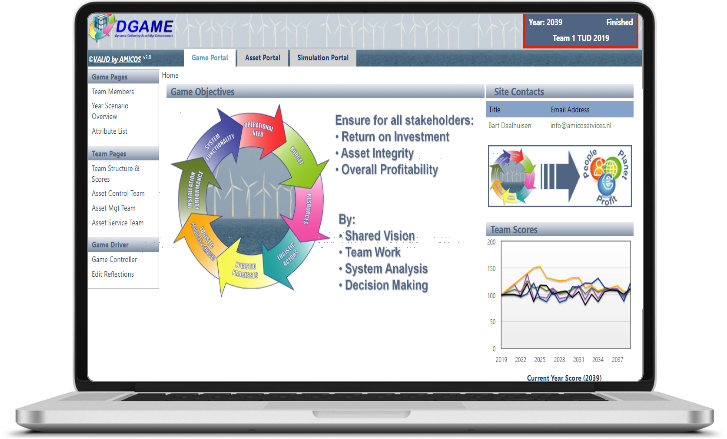
DGAME
DGAME is a serious gaming platform where team interests are central, because asset management is more than just Operations & Maintenance!
Experience the opportunities and threats that arise with Operations & Maintenance (O&M) of an offshore wind farm! DGAME offers a unique game environment in which participants get the chance to set the course for Operations & Maintenance in one of the most dynamic and challenging sectors where asset management is applied independently (DGAME1) or in a team (DGAME2). With DGAME you can train, refresh or develop insight and skills in the field of asset management.